7 Actionable Ecommerce Tips to Improve Your Organic Revenue
Key Takeaways
Restructure Product Groupings and Collections
Use your product names and category keywords in your metadata (especially the title)
Use your product names and category keywords in your H1’s
Reduce Keyword Cannibalisation and duplicate collections
Developing an Internal Linking Strategy
Google Merchant Centre optimisation
Image optimisation
You’d be surprised how many ecommerce stores haven’t implemented the basics of SEO. Generally, it’s because they’ve had a new store built without any input from an SEO team, or perhaps they’ve been focusing on growing paid and social channels.
In this article, we’ve collated 7 actionable ecommerce SEO tips, all of which are easy ways to help ecommerce businesses stimulate organic growth and revenue with simple changes.
1. Restructuring Product Groupings and Collections
Tip one sounds incredibly simple, but it's also a powerful way to improve the way your products are grouped as well as providing opportunities
Typically, ecommerce search results show groups of products in product category pages. This is what users expect to see so that they can browse through the collections.
It also makes sense that currently, Google gives preferences to category/collection pages for various searches:
Grouping your products together into collections or categories and using those groups as the focus for your SEO activities makes a lot of sense. The first step of any successful ecommerce campaign is to ensure your products are organised into collections. Better still, use keyword research to figure out what collection phrases your users are searching for and create dedicated collection pages to target these groups of phrases.
2. Use your product names and category keywords in your metadata (especially the title)
Leaving your ecommerce back-end to auto-populate your metadata? Don’t! While metadata tags might seem a little obligatory, they’re actually a very important ranking factor, boosting the visibility of your content and augmenting your search engine position.
Here’s a quick summary of quick, simple ways to optimise your metadata:
Title tags are concise but descriptive and should feature the most relevant keywords to the content on that page. Your title tag is the first thing a viewer sees in their search results, so even though you only have about 50 or 70 characters, you should use them wisely.
Meta descriptions should normally be a maximum of 250 characters, if not less – go for a less is more approach to avoid Google cutting off the end of your description. Remember that meta descriptions do not contribute to rankings, and Google can change the metadata shown, but it’s worth populating.
Unique meta titles and descriptions on each of your core product and category pages to ensure you don’t end up with competing pages (read more about keyword cannibalisation below).
Picking highly relevant keywords and posting them organically into your metadata is also time well spent, where it becomes more obvious what the page is about, ensuring your products are shown to a greater number of search users.
3. Use your product names and category keywords in your H1’s
Next, let's think about your H1 title tags. In short, you can use several 'categories' of headings on your pages, starting with an H1, which is your primary title.
Although some ecommerce stores assume that more H1 headers mean more space for keywords, this can be counterintuitive.
The best practice is to use one H1 tag on each page, clearly describing what the page is about (using your pre-agreed keywords).
Your title should be unique – never replicate the same header on multiple pages, since search engine bots might assume they're all identical, missing out entire pages and product categories.
Although an H1 tag is fairly short, you can be creative, crafting headers that are closely aligned with the products you’re showing or the information you’re sharing.
4. Reducing Keyword Cannibalisation
What does keyword cannibalisation mean? It means that you’re optimising more than one or several pages on the same website for the same keywords.
Even if the products are similar, having several pages optimised for the same keyword topics - inevitably means that all your e-commerce website pages rank lower than they otherwise would.
A note from an Expert: “Many of the e-commerce business owners we speak with rely on their platforms, like WordPress or Shopify, to identify high-ranking keywords. In itself, that's fine, but out of the box, duplication can occur on a product category level.” Mike Alexander, Ecommerce SEO Lead.
You may have several product categories with the same products, using the same H1 and metadata and featuring the same content. For example, Shopify often duplicates the product category page for each ‘tag’ or variation of the product. Example:
www.store.com/main-category/collection/ (Main collection page)
www.store.com/main-category/collection/blue (Duplicated page)
www.store.com/main-category/collection/green (Duplicated page)
it's essential that you implement processes for reducing this cannibalisation to reduce ranking fluctuations and competing pages.
5. Developing an Internal Linking Strategy
Our fifth recommendation is to ensure you’re using internal linking within your store so that related categories and products link to each other.
There are lots of good reasons to do so, including strong site architecture and highlighting the most important pages to search engine bots so they know which matters most and providing additional context to Google.
Lots of businesses assume that link building only applies to external links, but adding a few strategic internal links can really enhance rankings and traffic.
You can try linking from your navigation menu to core categories, adding links within your category content to point to related collections, or linking to core pages in blog posts.
6. Don’t forget your Merchant Centre optimisation
A simple product-related Google Search will show a feed of products above the traditional organic listings. This is called the Google Merchant Centre and contrary to popular belief, this traffic is classed as organic rather than paid:
Google Merchant Center is a tool that allows businesses to upload, submit and manage their store and product data on Google. This data is then used for various Google services, including Google Shopping, which displays product listings directly in search results.
These visual results provide high click-through rates due to their visual nature. Google Shopping ads appear at the top of search engine results pages, even before traditional text ads and organic listings. This high visibility can lead to increased traffic and conversions.
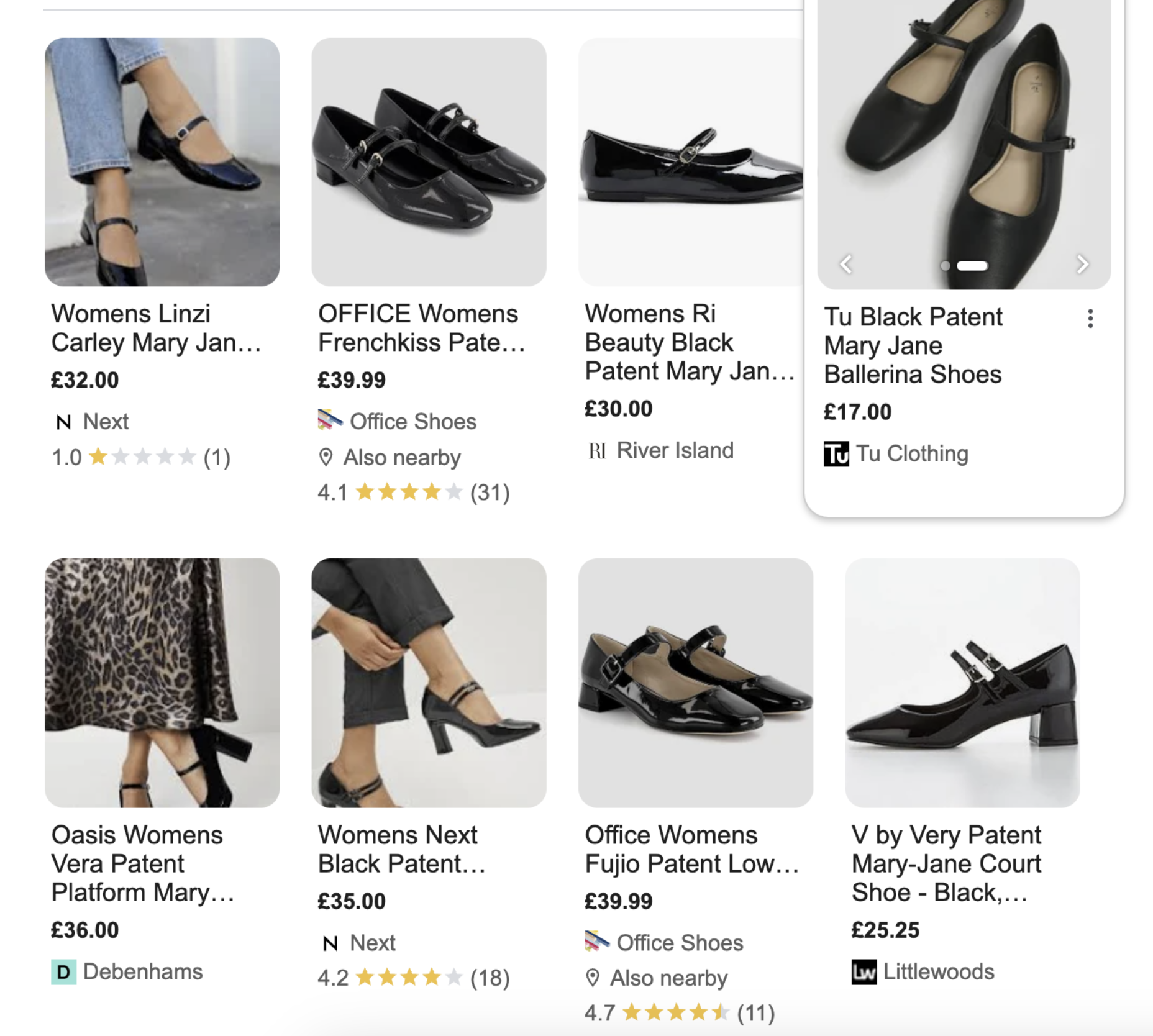
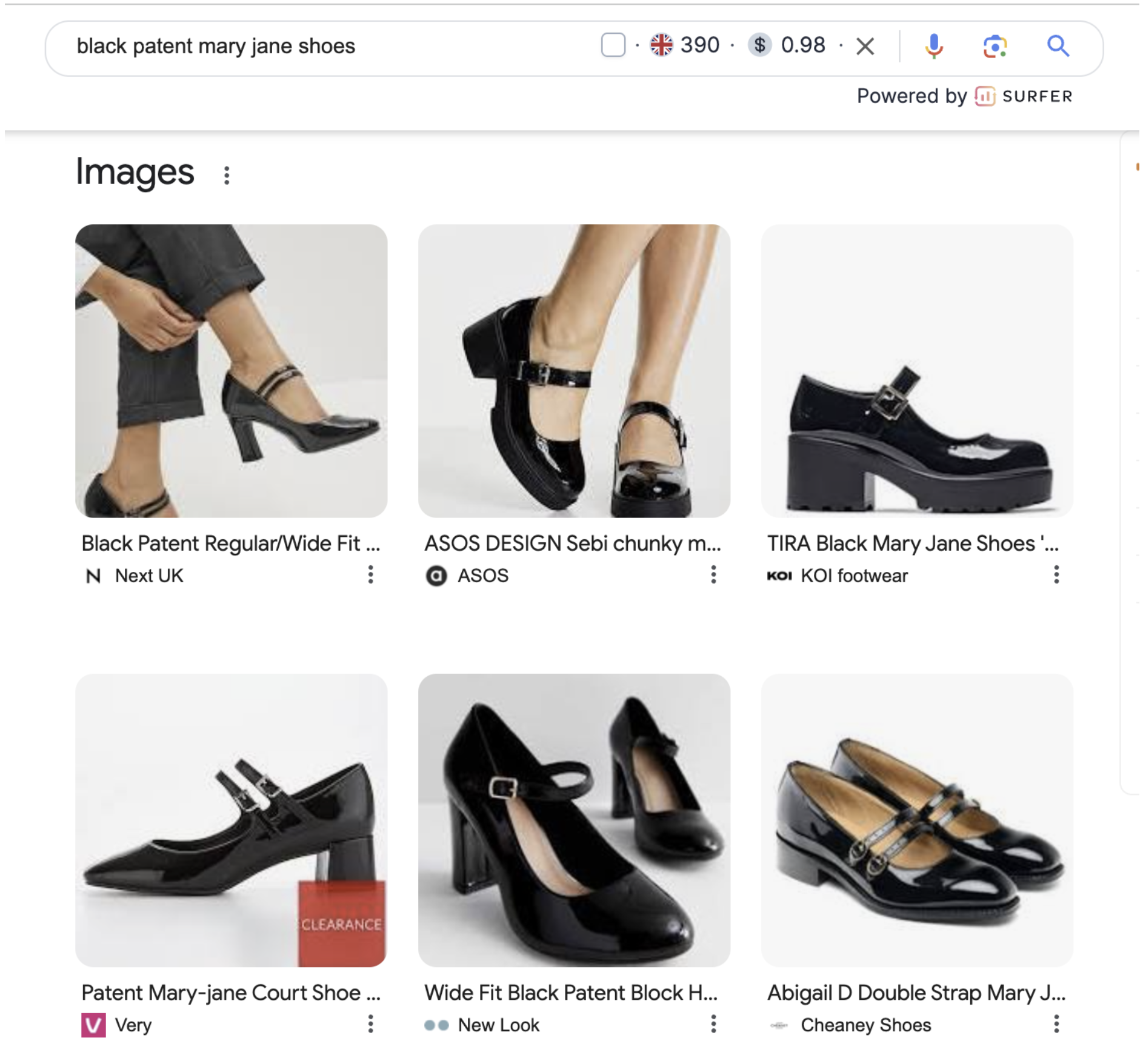
7. Focus on image optimisation
Google understands that some products are very visual items - purchase decisions are made due to the appearance of the product. Think fashion, jewellery or home decor. In response to this, image results are often front and centre for any ecommerce query. They’re usually found in a tiled format (see below):
Google Product Listing
Similarly to the Merchant Centre, images dominate search real estate on both mobile and desktop, so it’s important to optimise your images to give them the best chance to rank in image packs. This means descriptive alt tags and file name optimisation.
Are you searching for an ecommerce SEO agency in Manchester? Get in touch with One Day today. We can analyse your current rankings, visibility potential and on-site optimisation opportunities for increased organic sales.