Location-Based Advertising: A Deep Dive
Key Takeaways
Location‑based advertising uses geotargeting to serve ads to users in defined areas via GPS, Wi‑Fi or IP data, and can be applied across traditional outdoor media and digital platforms.
Advanced methods such as georetargeting and geoframing provide refined audiences, while geofencing and beacon technology are rarely used due to cost and scalability; campaigns must address privacy requirements.
Benefits include precision targeting and contextual messaging – referencing local landmarks or events increases relevance – but brands should consider higher costs and ensure data accuracy and ethical practices.
Location-based advertising (LBA) is a marketing strategy designed to deliver tailored advertisements to users based on their geographic location. Utilizing technologies like GPS, Wi-Fi, and IP addresses, businesses can reach potential customers with content that’s relevant to their location, often resulting in improved engagement and conversion rates.
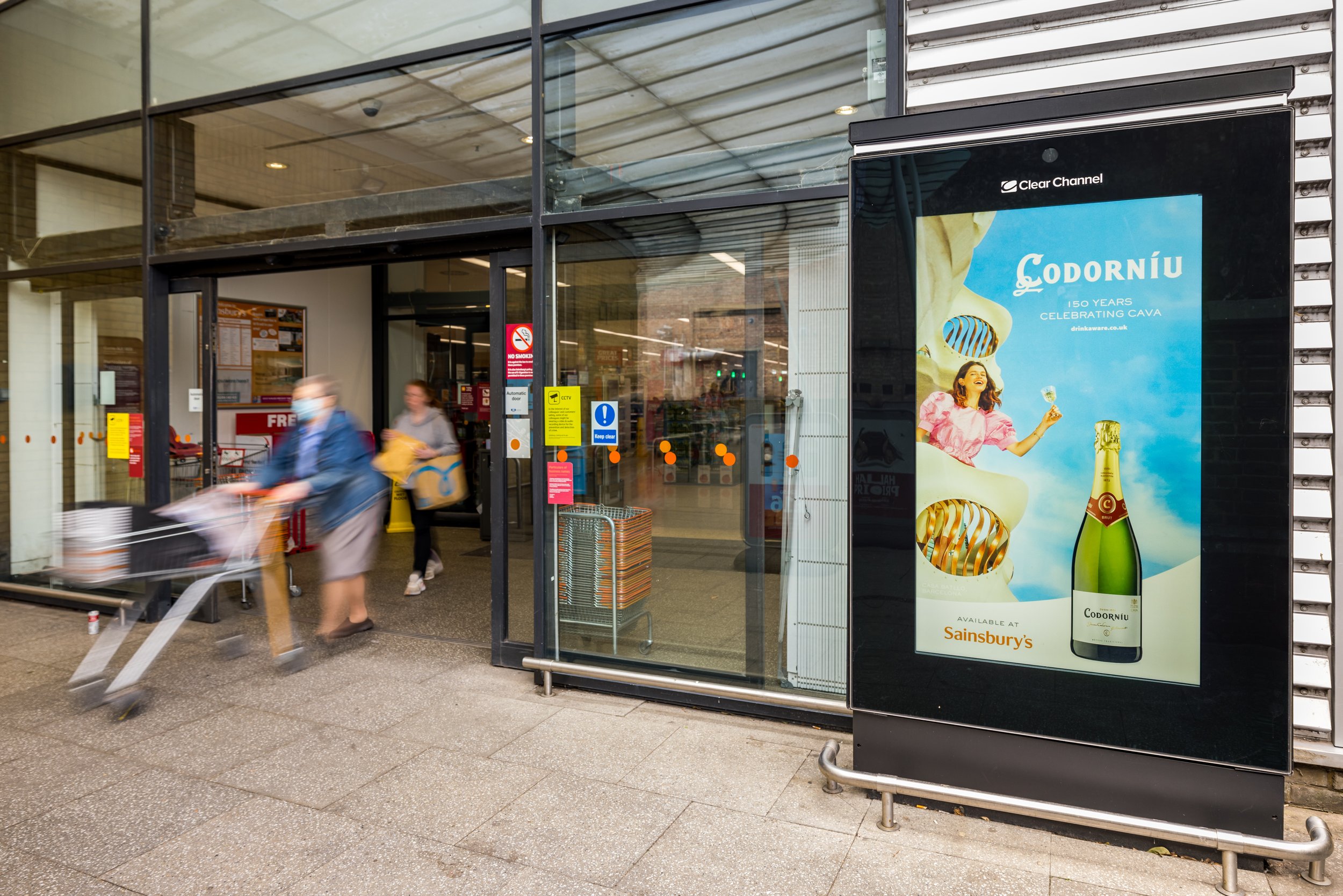
Example of geolocated outdoor advertising, see Sainsbury’s logo on the artwork.
Types of Location-Based Advertising
Geotargeting: The Core of Location-Based Advertising
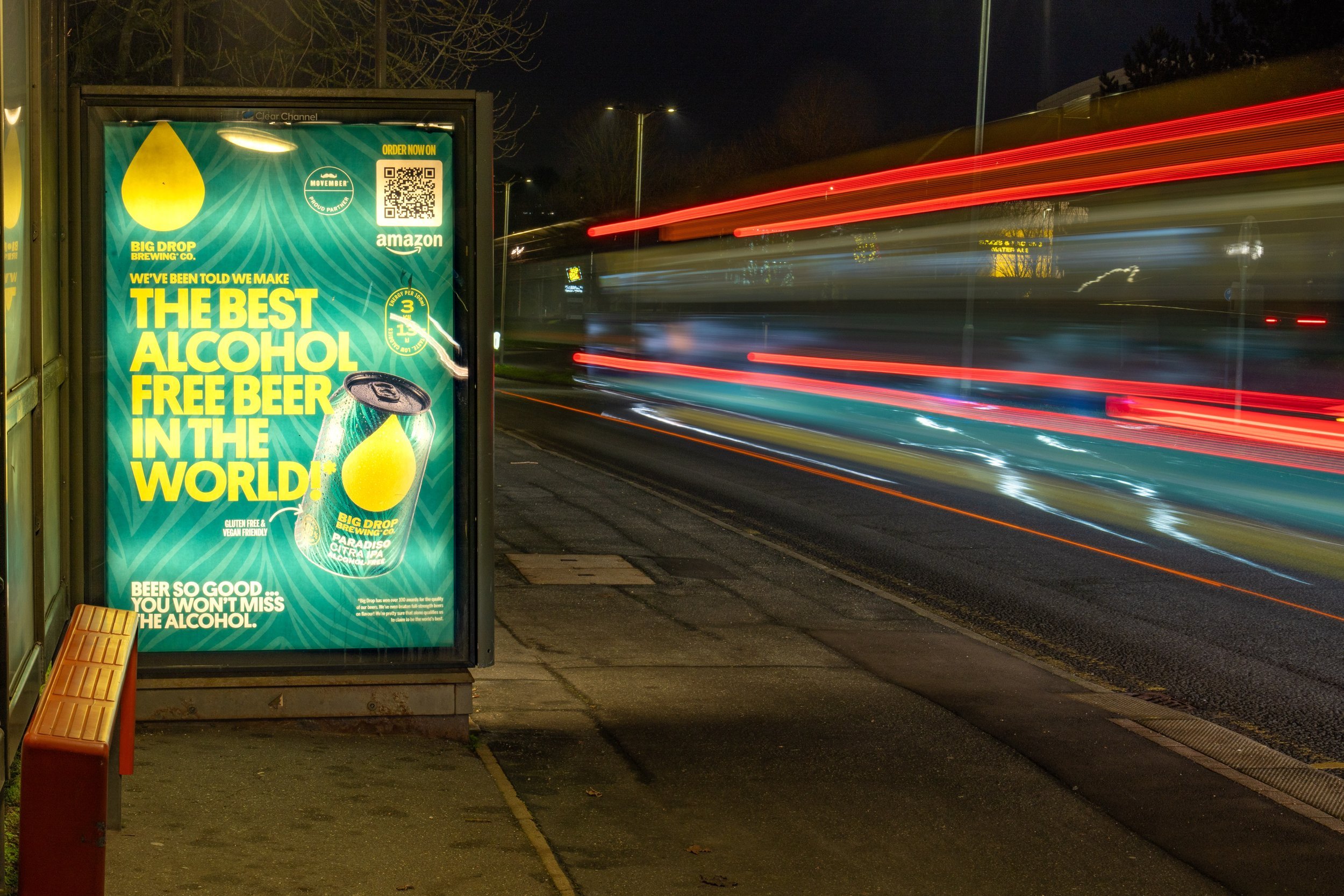
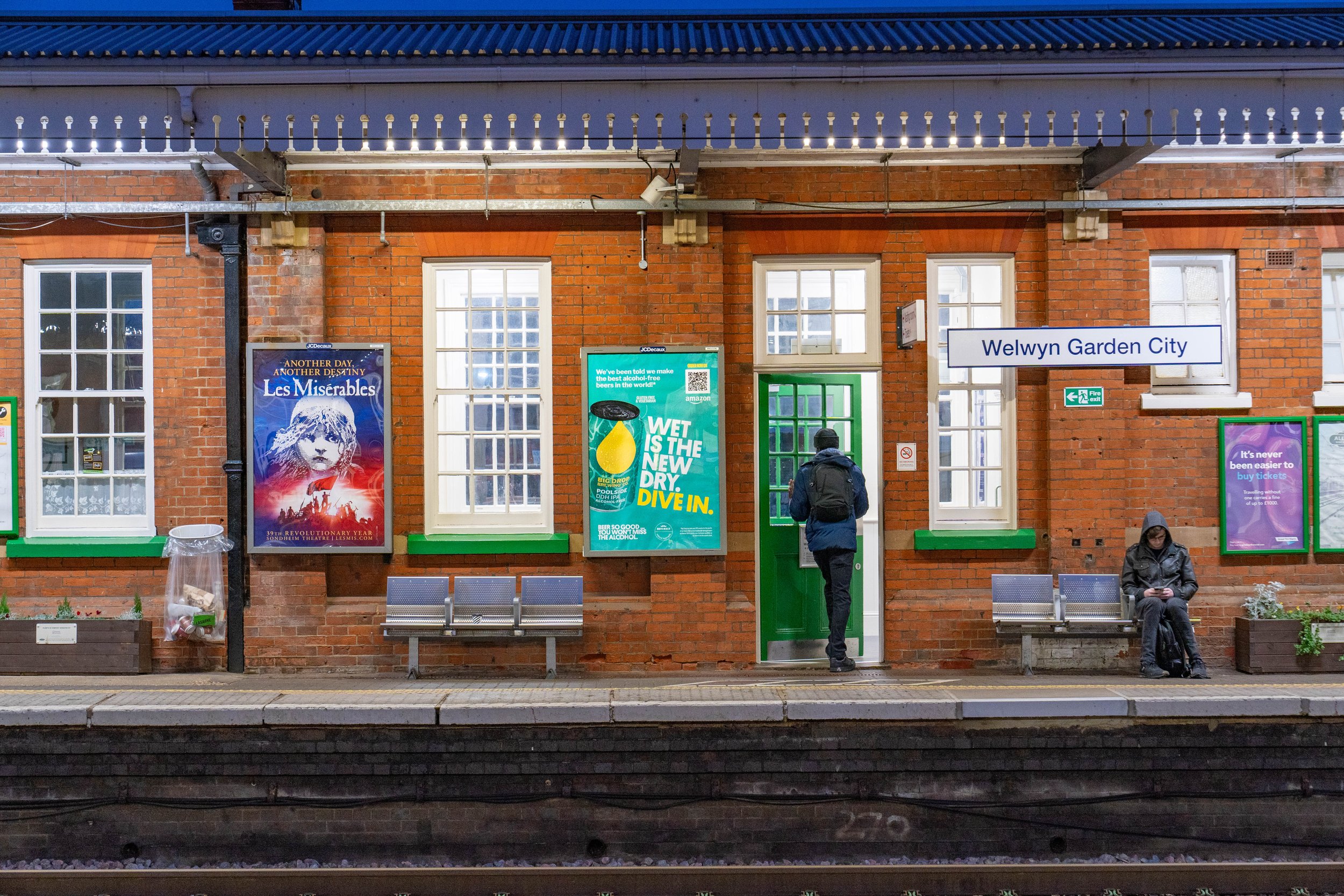
Geotargeting involves delivering ads to users within a defined geographic area, such as a city, neighbourhood, or specific radius. This approach is highly versatile and can be applied across various advertising channels, including traditional outdoor media and digital platforms.
Traditional Advertising: Billboards and posters can incorporate geotargeting by placing ads near relevant locations. For instance, a coffee shop might advertise its morning specials on a billboard close to commuter-heavy areas.
Digital Marketing: Ads on social media or search engines can target users based on their current or recent locations. While highly effective, this strategy can increase costs due to the precision targeting and competitive bidding for these audiences.
Geofencing (Not Really Used in Advertising)
Geofencing, often misunderstood as a widely used tool, involves setting up a virtual perimeter around a location and triggering ads when users enter the area. However, this technology is rarely deployed in retail or advertising due to its logistical challenges, high costs, and lack of scalability. Instead, businesses rely on broader geotargeting strategies that are more feasible and cost-effective.
Beacon Technology (Not Really Used in Advertising)
Beacon technology, another overhyped method, uses Bluetooth to deliver ads to users nearby. While theoretically promising, it has seen little practical application in advertising due to infrastructure requirements and limited user adoption.
Addressing Privacy Concerns (Not a Real Barrier)
Modern location-based advertising operates within strict privacy frameworks. Data used for these campaigns is sourced from trusted partners and complies with all relevant privacy laws and policies. Businesses ensure transparency and consent, eliminating significant privacy concerns and maintaining consumer trust.
Enhanced Engagement Through Contextual Messaging
One of the key advantages of location-based advertising is its ability to resonate deeply with audiences through relevant messaging. By incorporating location-specific elements, such as naming a city or referencing local landmarks, businesses can create a stronger connection with their audience. For example:
A digital ad for a pizza delivery service in London might say, “Get the best pizza in Soho tonight!”
A billboard near a sports stadium could read, “Celebrate the game with a cold drink — just down the road!”
This relevance not only grabs attention but also increases the likelihood of conversions.
Benefits of Location-Based Advertising
Precision Targeting: Reaching the right audience at the right time improves campaign efficiency.
Improved ROI: Focused campaigns minimise waste and maximise returns.
Relevance: Messages tailored to a specific location are more likely to engage audiences and drive action.
Challenges and Downsides
While location-based advertising is powerful, it’s not without its challenges:
Cost Implications in Digital Marketing: Highly targeted campaigns often come with increased costs, particularly in competitive markets.
Accuracy Requirements: The effectiveness of location-based advertising hinges on precise location data. Inaccuracies can result in irrelevant messaging, diminishing effectiveness.
Conclusion
Location-based advertising is an evolving field that combines technology and strategy to deliver personalised and timely messaging. By focusing on proven methods like geotargeting, integrating location-specific messaging, and maintaining ethical data practices, businesses can harness their full potential to drive engagement and conversions.